with Jupyter Notebook, Pandas, NumPy, Matplotlib, Scikit-Learn, SciPy, Keras, TensorFlow, Theano and datascience, OpenPyXL, and more…
First, be sure to install Python3 on macOS or Windows since the operating systems do not include Python3 by default. The underlying macOS operating system still runs primarily on Python2 and Bash and Windows underlying scripting language is Batch and Powershell.
There are two ways to install Python3 on macOS:
There are two ways to install Python3 on Windows 10:
- Installing Python3 from the Windows command line using the Microsoft Store
- Article Coming Soon: Installing Python3 on Windows subsystem for Linux (WSL)
Creating a Virtual Environment (venv)
Create the Virtual Environment. It has been suggested to put the venv directory in a hidden folder within your home directory. The reason to locate it there is to keep it separated from the code as well as to avoid placing it into sync locations such as Google Drive, Box, DropBox, etc. All your venvs will be located within your home directory following an easy to use naming pattern. To generate the virtual environment run this command:
macOS: python3 -m venv ~/.venv/project_name_venv
Windows: python3 -m venv %userprofile%\.venv\research
Now that the virtual environment has been created you may activate it by executing:
macOS: source ~/.venv/project_name_venv/bin/activate
Windows: %userprofile%\.venv\research\Scripts\activate.bat
upon execution your terminal command prompt will change to include the (venv) name. Any Python packages you install within the venv are contained only within the venv and do not effect the system-wide packages. Note, each time you return to your computer, you will have to activate the venv when you would like to use it.
Once you have enabled your virtual environment you may upgrade your pip version by running:pip install --upgrade pip
Install and configure Jupyter Notebooks
The Jupyter Notebook module provides an open-source web application that creates notebook documents ideal for learning and writing Python data manipulation and data science.
pip install jupyter
pip install jupyterthemes
Later on when we load Jupyter notebooks, your notebook by default will be on a light background with dark foreground text.
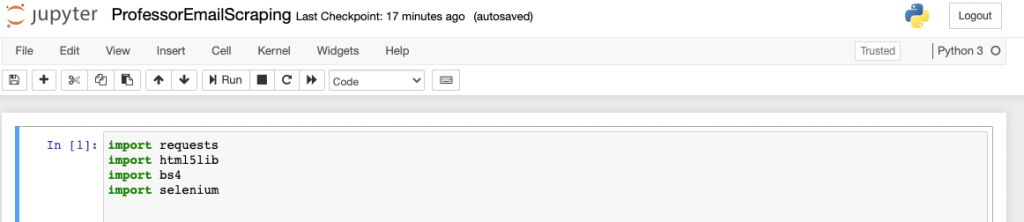
If you like the standard white background/dark text foreground style of editing documents you do not need to change the theme. If you would like to change the theme to dark mode you may try out chesterish or monokai theme as follows.
#list themes
jt -l
#set a theme using the jt -t "theme" command as follows
jt -t monokai
When loading Jupyter your notebook will now appear using a dark theme.
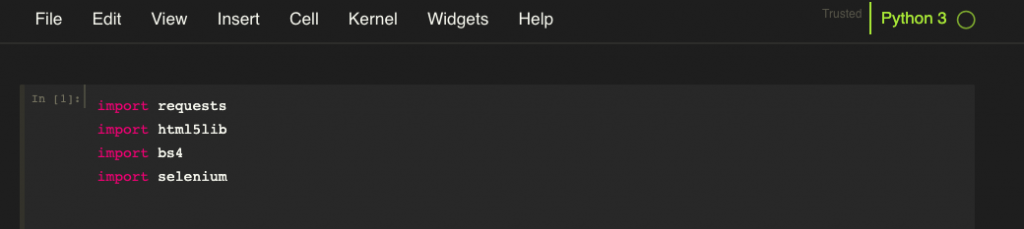
# some folks like the following detailed theme settings:
jt -t monokai -f fira -fs 10 -nf ptsans -nfs 11 -N -kl -cursw 2 -cursc r -cellw 95% -T
# only run the following if you do not like the current theme
# to reset Jupyter to the default theme run:
jt -r
Installing Data Science Python Modules
Let’s now install the data science related Python Modules:




![]()
pip install pandaspip install datasciencepip install scikit-learn
Install Excel 2010+ File Read/Write Functionality
pip install openpyxlpip install xlrd
Install Common Machine Learning Packages



If you will be working with neural networks, machine learning (ML), and matrices, also load the following packages.
pip install keraspip install tensorflowpip install theano
Core Packages Installed Automatically with Above Packages


Note: numpy, matplotlib, scipy, and many other packages will automatically be installed when executing the above package installs.
Additional Essential Must Know Python Libraries from the Python Package Index (PyPi)

If you are working with dates and times, the Pendulum package is superb, offering immense functionality for manipulating and creating date related Pendulum objects.
pip install pendulum

If you will be performing web scraping or otherwise interfacing with websites, the requests library adds significant functionality for automatic content decoding, session objects with persistent cookies, connection timeout management, authentication, etc.
pip install requests


Often when scraping data from the web you will need extract information from HTML pages. This process is known as parsing. The html5lib and beautifulsoup4 libraries were designed specifically for making scraping information from webpages easy.
pip install html5lib
pip install bs4

The wget package is a utility for non-interactive file downloads from the web. It supports HTTP, HTTPS and FTP protocols.
pip install wget

The Selenium package is used to automate interaction with the web browser. When scraping data from the web, often the data is not directly presented on a single page load. This means you will have to invoke key stroke or other commands in order to pull the data you are targeting.
pip install selenium

If you will be working with files, the PyFilesystem package creates a simpler, easy to maintain, concise, abstraction to file interactivity. If you use this add on package and the location of your file resources changes in the future, it is easier to update the code, even if the files move between platforms, either locally over a variety of network protocols.
PyFilesystem has the capability of interacting with the local operating system file system, accessing files stored inside of Zipped files, accessing files over FTP, etc.
pip install fs
Reviewing PIP Packages That Have Been Installed.
pip list
will output a complete list of all packages that have been installed into your current environment.
Getting Started with Python3 using Jupyter Notebooks
Now that you have installed Jupyter notebooks and many data science related modules you may now interact with Python 3 via the terminal or from within Jupyter notebooks.
Lets get started with Jupyter! Create a directory folder for your new project or navigate into the directory of an existing project. Always do this to minimize the scope of what the Jupyter local web app has access to on your system.
To begin programming in Jupyter notebooks, type:jupyter notebook
Running the Jupyter app will disallow you from entering any further commands into the terminal. If you would like to run any additional terminal commands while Jupyter is open, press CMD + T to open up a new terminal tab on macOS or if you are using windows, open up a new CMD prompt. Be sure to re-enter the desired virtual environment as described above using the source command.
Note: To quit the running Jupyter process, from the terminal command line press CTRL + C. You will then be prompted as follow.

Press Y to shut down the notebook server.
Note: If you close the Terminal (MacOS & Linux) / Command (Microsoft) window, you will have to reactivate the virtual environment next time you open a new one.
macOS: source ~/.venv/project_name_venv/bin/activate
Windows: %userprofile%.venv\research\Scripts\activate.batNote: If you want to add additional Python packages, you must quit out of the running Jupyter process as described in the previous section. Run the pip install command as desired, then restart jupyter notebooks.
Happy Computing!